In the dynamic world of e-commerce, understanding the nuances of various business models is crucial for success. This article delves into the core differences between two prominent models: Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C). By exploring the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of these distinct approaches to online commerce. Whether you are a budding entrepreneur, a seasoned business owner, or simply curious about the online marketplace, grasping the distinctions between B2C and C2C will equip you with valuable insights.
B2C e-commerce, a widely recognized model, involves transactions between businesses and individual consumers. Conversely, C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers, often through a third-party platform. This article will dissect the key features that differentiate B2C and C2C, examining aspects such as target audience, marketing strategies, payment processing, and logistical considerations. By understanding these critical distinctions, you can make informed decisions about which model best aligns with your business goals or personal needs within the e-commerce landscape.
Defining B2C and C2C E-commerce
Business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce refers to the online sale of goods and services directly from businesses to individual consumers. This model is characterized by a business acting as the seller, and an individual making a purchase for personal use. The transaction is typically straightforward, with the business setting prices and managing the sales process.
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce, on the other hand, involves transactions between individual consumers. These sales often take place through online marketplaces or platforms that connect buyers and sellers. In this model, individuals list items for sale, and other individuals purchase them. The platform typically facilitates the transaction and may offer services such as payment processing and dispute resolution.
Characteristics of B2C Businesses
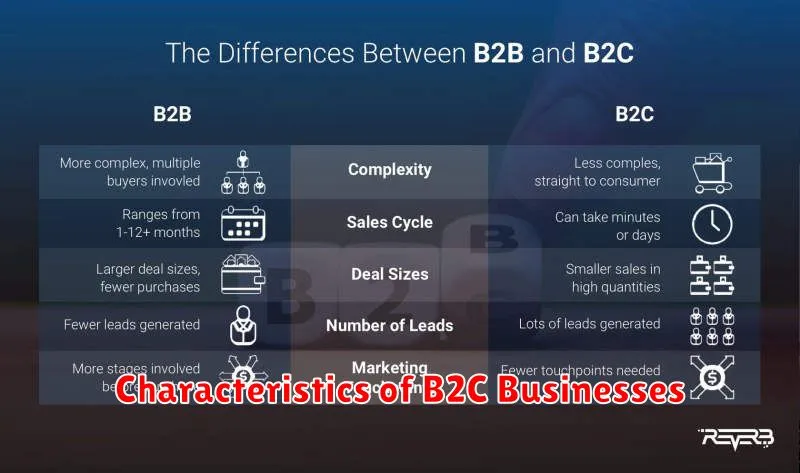
B2C businesses exhibit distinct characteristics that differentiate them from other e-commerce models. A primary feature is the direct selling of products or services to individual consumers. These businesses typically maintain a higher sales volume with lower individual transaction values compared to other models.
Strong branding and marketing efforts are essential for B2C companies to attract and retain customers. They often focus on creating emotional connections with consumers through targeted advertising and engaging content.
B2C operations often involve streamlined logistics and fulfillment processes to handle large volumes of orders efficiently. Customer service plays a crucial role in building loyalty and managing consumer expectations.
Another key characteristic is the emphasis on user-friendly online interfaces and shopping experiences. This includes intuitive website navigation, secure payment gateways, and personalized recommendations.
Examples of B2C E-commerce
Numerous businesses operate within the B2C e-commerce model, spanning various industries and product categories. Understanding these examples provides a clearer picture of the model’s breadth and impact.
Retail Giants: Large online retailers like Amazon and Walmart exemplify the B2C model. They offer a vast selection of products directly to individual consumers.
Specialty Stores: Online stores specializing in particular niches, such as clothing boutiques (e.g., ASOS) or electronics retailers (e.g., Best Buy), focus on a specific customer base with tailored product offerings.
Digital Content Providers: Services offering digital goods like music streaming (e.g., Spotify), online courses (e.g., Coursera), and software downloads (e.g., Adobe) are prime examples of B2C e-commerce in the digital realm.
Grocery Services: Online grocery platforms like Instacart and grocery delivery services offered by supermarkets (e.g., Kroger) are a growing segment of the B2C market, offering convenience and direct-to-consumer delivery.
How C2C Works
C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers, often using a third-party platform as an intermediary. This platform provides the infrastructure and services necessary for buyers and sellers to connect and conduct business.
Typically, the seller lists their item on the platform, providing details such as a description, price, and images. The platform may offer features like listing templates, secure payment processing, and dispute resolution services. Buyers can browse or search for specific items, and communicate with sellers through the platform to ask questions or negotiate pricing.
Once a transaction is agreed upon, the payment is typically processed through the platform, which often holds the funds until the buyer receives and accepts the item. This helps protect both parties involved. After successful delivery and confirmation, the platform releases the funds to the seller, deducting any applicable fees.
Advantages and Disadvantages of C2C

Advantages of C2C
C2C e-commerce offers several compelling advantages for both buyers and sellers. Lower prices are often a major draw for buyers, as individuals selling used or unwanted items typically price them lower than retail stores. Wider selection is another benefit, with niche or hard-to-find items frequently available. For sellers, C2C platforms provide a convenient way to reach a broad audience and declutter or sell unwanted possessions. The low barrier to entry makes it easy for anyone to become a seller.
Disadvantages of C2C
Despite the advantages, C2C e-commerce also presents some challenges. Lack of quality control can be a major concern, as products are not typically inspected or verified. Limited buyer protection is often a drawback, as transactions occur between individuals, making disputes and refunds more complicated. Security risks, including fraud and scams, are a potential concern. Finally, shipping logistics can be complex and often left to the individual seller, potentially leading to delays or issues.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Selecting the right e-commerce model is a critical decision that impacts your business strategy, operations, and overall success. Several factors should be considered when evaluating B2C versus C2C models.
Firstly, consider your product or service. Are you offering a standardized product suitable for a wide audience (B2C), or does your business model benefit from the unique and diverse offerings of individual sellers (C2C)?
Scalability is another key factor. B2C models often require significant upfront investment in inventory and logistics, impacting initial scalability. C2C platforms can scale more rapidly as inventory management is distributed among individual sellers.
Finally, evaluate your desired level of control. B2C businesses maintain greater control over branding, pricing, and customer experience. C2C platforms offer less direct control, relying on community guidelines and seller reputations to govern the marketplace.
By carefully weighing these factors, businesses can make an informed decision about which e-commerce model aligns best with their specific needs and objectives.